Alcohol affects the brain in it’s entirety and in certain areas in particular.
Alcohol is a drug and hence drugs work on all brain cells, making the communication between neurons slow. The brain cells are functioning differently. Eventually there will be brain cells lost. The loss of brain tissue is very clear from the daily drinking of 6 glasses. This loss has to include the fact that alcohol is toxic to brain cells and deficiencies of vitamin B1, due to alcohol. After some years, excessive drinking creates shrinkage of the brain. In very heavy drinkers, a level of 10 to 15% decrease occurs after 10 to 15 years.
Alcohol has a strong influence on the frontal cortex (front part of the brain). This section is responsible for self and social functioning, but also of purpose, reason and solving problems. Damage to the frontal cortex is thus responsible for a decline in intellectual abilities. By reducing the self, one is more likely to be less impulsive with regards to reactions and inhibitions, among other things, you’ll continue to go drinking.
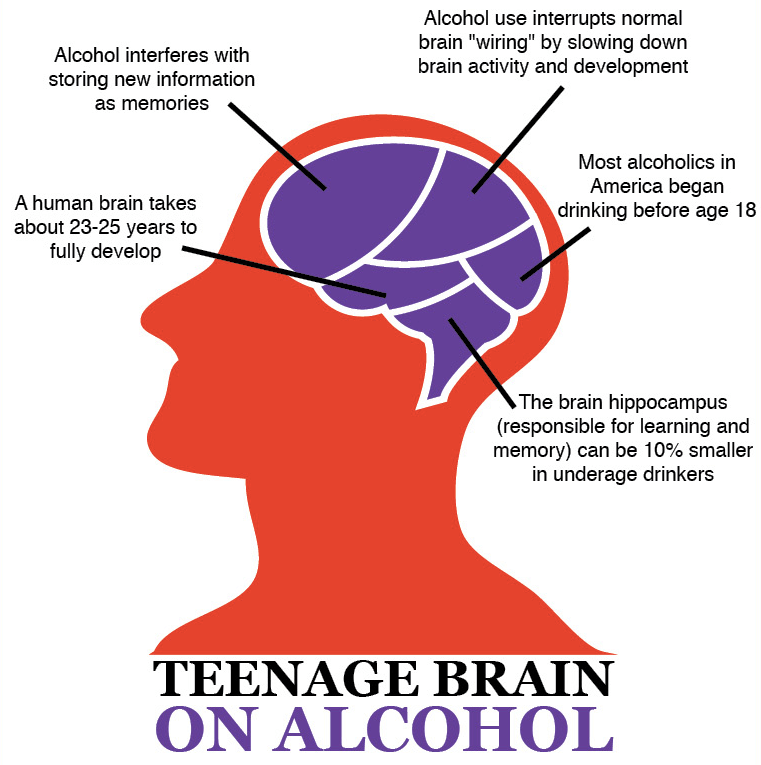
The effect on the hippocampus is that reminders of the short-term memory is not transferred to the long-term memory. This causes blackouts. Drinking over a ling period of time often has a significant impact on memory function in general.
The impact of alcohol on the cerebellum (small brains, the back of the head) creates disturbances in motor control, coordination and balance. This is already apparent when you stumble and can’t walk properly after drinking. Prolonged excessive drinking can sometimes lead to permanent damage.
The medulla in the brainstem is responsible for a number of autonomic functions like breathing and heartbeat. When this section is effected by too much alcohol and drugs,coma can occur and you can die. Especially binge drinkers who drink large amounts of alcohol quickly, run this risk.
The pituitary is a gland located in the main subject is the brains. The pituitary is responsible for a substantial number of hormones, including growth hormone. Many drinking at a young age can result in stunted growth fueling.
The brains develops up until you are about 25 years old. Until then, it is particularly vulnerable to toxic effects. Excessive drinking from an early age can cause irreparable damage. This causes that the thought processes, memory and self esteem is negatively affected.
- Everything You Think You Know About Addiction Is Wrong
- Top Alcohol Rehab
- What Is Alcohol Rehabilitation?
- Finding Quality Treatment
- Effective Alcohol Rehab Programme
- Is It Safe To Drive The Morning After Drinking Alcohol?
- Types Of Alcohol Rehab
- Folic Acid Deficiency & Pregnancy
- Alcohol Rehab And Physical Recovery
- Alcoholism TreatmentI
- Alcohol Rehab Myths
- Effects Of Alcohol On The Body
- Best Alcohol Rehab
- Do I Need To Go To An Alcohol Rehab?
- Alcohol Group Support & Treatment Options in South Africa